According to statistics, the number of infertile couples dreaming of their own child to no avail is steadily increasing every year. Disappointing figures are not able to correct even modern reproductive technologies: certainly, in vitro fertilization, especially with the use of microsurgical techniques, gives positive results, but it is not a panacea. What is the reason for such a picture, how does female and male infertility develop and what diseases can lead to it? Answers to these questions will help to better understand the actual problem of reproductive dysfunction and, if possible, prevent its development with timely and high-quality medical care.

Background: What does infertility mean?
In medicine and reproduction, there is still no clear framework for a disappointing diagnosis – in most cases, the inability to conceive a child is reversible, which means that a disease that makes conception and gestation difficult can be successfully overcome. However, the first suspicions of infertility appear in the event that a married couple leads an active and regular sex life without the use of contraception, and pregnancy does not occur within one year. This period may be extended taking into account the individual reproductive capabilities of partners, for example, age, ovarian reserve or sexual characteristics.

A few decades ago, it was believed that the diagnosis of infertility and the diseases causing it may be related only to a woman, but today’s data show that the problem may lie in the health status of both partners. What diseases cause a decline in male and female fertility and how to minimize the likelihood of infertility? Let us consider in more detail the features of reproductive problems of women and men.
Fertility factors
Diseases leading to infertility can affect any system in the body, and it does not matter at all whether it has a direct bearing on sexual function or not. The fertile capabilities of both spouses are directly related to their age, lifestyle, psychological stability, the level of stress to which they are exposed, the ecological situation and hundreds of all sorts of factors that somehow affect the processes of conception. Moreover, even a 100% healthy person (which is practically unreal!) Can face reproductive problems – simply their reason will lie not in the physiological, but in the psychological plane.

The most common diseases that cause infertility, regardless of gender, are:
- Hormonal abnormalities. Malfunction of the endocrine system affects the activity of the whole organism, so it is not surprising that amid such an imbalance, sperm activity or egg maturation changes.
- Infectious processes. Against the background of active inflammation or a sexually transmitted disease and proceeding in a latent form, changes in the reproductive sphere may develop that prevent the conception and bearing of the child.
- Pathology of the structure of the urogenital system. Congenital or acquired physiological abnormalities affecting the reproductive system can reduce the likelihood of a successful pregnancy, and in some cases even lead to irreversible infertility.

- Habits affecting reproduction. Not only diseases can lead to infertility – similar problems often cause a wrong lifestyle. Alcohol abuse, smoking, chronic overeating and even lack of sleepwear out the body, causing internal exhaustion and reduced functionality. It is not surprising that a decrease in fertility may develop against this background.
- Psychological factor. No matter how trite it sounds, psychology and physiology are directly related to each other. An internal barrier or fear of future changes, psychological unpreparedness for parenting, and subconscious insecurity in one’s own future can impede conception even in the absence of diagnosable diseases leading to infertility.
- External factors. An important role in the formation of pregnancy is the environment. The statistics say that residents of industrial cities and megacities suffer from infertility more often than their peers living in more prosperous regions from an environmental point of view.

Female pathologies leading to reproductive dysfunction
Despite the fact that infertility can be caused by both female and male factors, it is women who more often and earlier begin to “sound the alarm”, and not without a reason – as a rule, any deviation from the normal indicators of the expectant mother can provoke gynecological changes, negatively affecting pregnancy.
Having found out the source leading to infertility in women, one can make maximum efforts to eliminate it and restore reproductive function by taking adequate measures in a timely manner. As a rule, such changes most often consist of the following:
- Endocrine anomalies. The process of maturation of the egg, like the entire menstrual cycle, is completely controlled by hormones synthesized by the endocrine glands. It is therefore not surprising that any change in the concentration of hormones in the body of the expectant mother can lead to the inability to conceive a child or endure it. In addition, this imbalance can provoke endometriosis – another serious illness that leads to infertility. However, in most cases, the endocrine factor of infertility is not a sentence – even if it is impossible to cope with the imbalance, you can reconcile such changes with the help of synthetic analogs of hormones.

- Immunological abnormalities. If antisperm antibodies are present in a woman’s cervical mucus or blood, they can cause an inadequate response of the immune system to partner’s sperm and, as a result, impede the fertilization process.
- Anatomical pathology. Features of the anatomical structure that impede pregnancy can affect both the uterus itself and adjacent organs – fallopian tubes, cervix, ovaries, etc. The tubular factor is most often associated with the appearance of adhesions and low patency of the tubes, due to which even active sperm cells cannot penetrate the egg cell and lead to its fertilization. Adhesions may also affect the cervix, especially during surgery and pregnancy termination in history. Diseases localized in the uterus usually do not make it difficult to form the embryo, but to attach it to the endometrial tissues, which cause miscarriages in early pregnancy. Such changes are usually poorly amenable to therapeutic treatment, so many gynecologists recommend surgical removal of diseases.
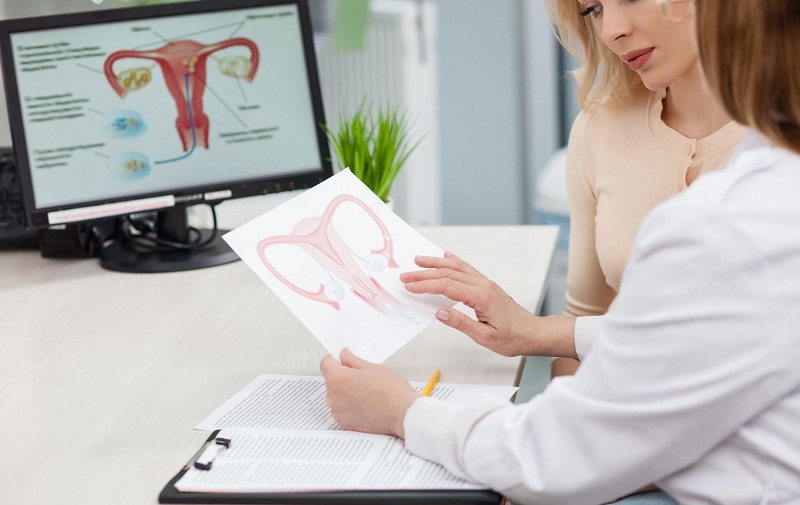
- Irreversible infertility. Unfortunately, some women by nature or for other reasons are not given to experience the happiness of motherhood: in the total absence of reproductive organs (congenital or acquired), the process of conception and carrying are impossible in principle, and therefore the only way out can be the services of a surrogate mother.
- Individual characteristics. The age factor, genetic predisposition to a low ovarian reserve, early menopause, constant stress, overwork, work in harmful conditions – the causes that reduce the likelihood of a successful conception and successful pregnancy.
The sooner the doctor can identify the disease leading to infertility and prescribe the correct treatment, the higher the chances of becoming pregnant. Therefore, it is not necessary to delay the diagnosis – at the slightest suspicion, it is better to “outbid” and pass all the necessary tests than to try to cope with serious complications.

Possible causes of male infertility
Male diseases play a key role in an average of 40% of the total number of childless couples. Such pathologies are easier to treat – even with only 1 healthy sperm, today it is possible to conceive a child using IVF using microsurgical techniques. Nevertheless, it is always better to try to solve the problem at the stage of its formation than to undergo a long course of treatment with the possible need for artificial insemination.
Male infertility is usually associated with the following factors:
- Diseases of the vas deferens. If a man has difficulty in ejaculation of seminal fluid, most likely, we are talking about excretory pathology. In this case, the quality, activity, and viability of spermatozoa do not matter – their penetration into the female body in a natural way, and hence, the onset of pregnancy is impossible or extremely difficult. It is possible to eliminate such pathology with the help of surgical methods – after a restoration of the patency of the ducts, the problem, as a rule, is safely resolved. Otherwise, the couple may require artificial insemination or IVF with a biopsy of the male seed.
- Deviations in semen reading. A qualitative or quantitative change in the composition of sperm is perhaps one of the most frequent male diseases leading to infertility. An insufficient number of sperm cells, their low mobility or the presence of structural abnormalities lead to the impossibility of conception or miscarriage of a deliberately hopeless pregnancy if it has nevertheless occurred.
- Immunology. Not only a woman’s body can produce anti-sperm antibodies – sometimes these components are found in a man’s blood. This autoimmune disease inhibits spermatogenesis and, as a result, leads to infertility.
It should be borne in mind that most often infertility is caused not by one, but by several diseases simultaneously affecting both male and female health. Therefore, the diagnosis of reproductive diseases should be carried out simultaneously with both partners – so the probability of a successful outcome increases several times.
Faced with reproductive dysfunction, you should not fall into despair – the possibilities of modern medicine, though not limitless, are quite wide, which means that in most cases such a diagnosis is not a sentence for a couple!


